windows 7 disk queue length 100
Server and Target may experience one or more of the following symptoms if Antivirus is not properly tuned for your Provisioning Services (PVS) environment: Target Device or Server appears sluggish or generally slower than normal. Prolonged, excessive CPU or memory utilization. Significant change in the Write Cache Disk I/O Performance. For example, when using Perfmon, the percentage of disk write time or disk write queue length increases significantly. The Target Device software indicates excessive retries in its console. In the console, Inventory shows that the replication status is incorrect for a vDisk. Target Device fails to boot to vdisk, rather boots to local disk and displays a red X on the client status tray. During boot, Target Devices performance remains subpar for a short time while AV definitions are updated. Symptoms may vary greatly and are not limited to this brief list. Limit Antivirus definition updates to only the Master Target Device or Update Target Device.
Create a plan to upgrade the vDisk periodically using manual or Automatic vDisk updates. This can significantly reduce network bandwidth and overall performance. Avoid scanning the vDisk Write Cache file and streaming disk IO that makes up the operating system for a given Target. Disk IO that has been altered, tampered, or corrupted should cause an application or operating system to fail immediately. Avoid scanning the following process and system drivers on PVS 6.x\7.x Target Devices: bndevice.exe: handles client functions, licensing, etcbnistack6.sys: IO protocol driver | UDP port 6911-6930CVhdBusP6.sys: disk enumeratorCNicTeam.sys: network teaming if being usedCFsDep2.sys: system minifilterCVhdMp.sys: mtorage miniport driver Avoid scanning, whitelist or permission the following processes on PVS Server 6.x\7.x: Streamprocess.exe: IO delivery | UDP port 6901-6910Streamservice.exe: watchdog for the streamprocessSoapserver.exe: handles Database connectivity and AD authenticationInventory.exe: vDisk Inventory |
the WC file names for target local disk cache are: 6.x: .vdiskcache7.x: vdiskdif.vhdx or .vdiskcache In general, most antivirus product defaults are configured to scan all files IO and\or processes on a disk.
windows 7 autoplay funktioniert nicht mehrLike an operating system that runs locally to its hardware, all PVS streaming IO operations are subject to real-time scanning until specified otherwise. If an antivirus program scans the continuously active data stream that consists of and delivers the operating system, then this impedes the normal operation of PVS by causing disk IO delays and read-write failures, HA problems, and so on. In extreme cases, the PVS Target Device and Server can consume more resources than necessary or become inactive. When a virtual disk is running in standard mode and needs to be restarted, it can potentially re-download all the previously loaded virus definitions;
best practice would be to update just the Master Target Device. This is a common scenario that causes serious degradation when Target Devices are restarted in mass, often causing bandwidth bottlenecks for a brief period of time. When installing or upgrading antivirus client software or any other software that alters the Target’s network stack, PVS 6.x\7.x. requires you to first uninstall the PVS Client Software and reinstall it last, prior to re-imaging. The PVS software becomes unusable if another software product alters or interferes with the Target's BNistack6.sys or the Servers streaming IO network interface. Antivirus software varies from vendor to vendor. Check with your Antivirus software vendor for specific instructions on configuring scanning exceptions. As always, it is recommended to test AV client software and its configuration prior to placing it into a Provisioned environment. Obtaining a performance baseline early may help prove useful in the event of troubleshooting.

Refer to the following for additional information: Recommended Antivirus Exclusions by Citrix ProductAntivirus Guidelines from CitrixAntivirus Software Configuration - Citrix GuidelinesReview firewall settings such as access control lists (ACL), or troubleshoot problems with network Free download try it now! Review firewall settings such This page will explain how to use performance monitor to log disk counters. recommend solutions to disk bottlenecks on Windows Servers (2003 or 2008). Firstly, a homily to explain why you should always monitor these 'big four' objects: Memory, Processor, Disk andBeware of monitoring one counter in isolation because that can lead to the wrong conclusions. One company thought they had a problem with slow disks on a Windows 2003 Server. monitor confirmed long queues and slow disk access times. conclusion was that the bottleneck was the disk and so they bought fasterUnfortunately, the slow response persisted and they called me in to

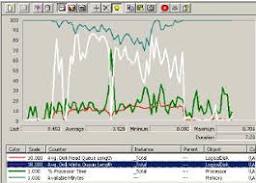
By monitoring all the 'big four' performance objects, I found excessive paging, there was also less than 2MB of available bytes. ailment was lack of memory, high disk usage was a symptom and not the cause. lesson: incomplete monitoring can mean a waste of time and money, so always record these four objects:- Memory, Processor, Disk and Network. The Windows server roles most likely to experience disk problems are, web servers with lots of graphics and file servers. On the other hand, Domain Controllers, DNS, or DHCP servers are unlikely to have disk bottlenecks In Diagram 1 performance monitor shows classic symptoms of a disk bottleneck. based on the Disk write queue counter, you can see that this queue averagesIn fact the average is nearly 4 (with a peak of over 8). I wanted to to be unbiased. So, to ensure that it was not a processor or memory bottleneck, I also recorded % processor time and available bytes. As you can see from Diagram 1, the processor's average was below 30%.
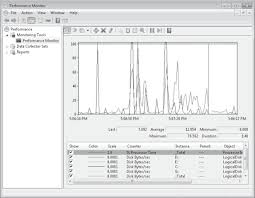
If the processor were the bottleneck the trace would be over 80%. other hand, if there was a memory shortage, available bytes should drop below 10MB. The graph show there was always 70 MB of Available MBytes.The performance bottleneck may be worse than the average figures above suggest. Diagram 2, I have legitimately chopped the graph to isolate the periodFor these 5 minutes (4:46) the average is almost 6 against the bottleneck threshold of 2.The other difference is Diagram 2 (taken from performance monitor), I have included % Disk Time, this exceeds 100% for the duration of the trace. In other words, the disk is working flat out writing data to to the hard drive.There is one more deduction we can make from the queue data on the chart. If you compare the white line with the thick green line near the bottom, you can tell that the disk is writing more rather than reading. To see the diagrams more clearly, double click and expand the thumbnails into larger diagrams.
will help you discover what's happening on your network. utility will also guide you through troubleshooting; indicate whether the root cause is a broken link, faulty equipment or Perhaps the NPM's best feature is the way it suggests solutions to networkIts second best feature is the ability to monitor the health of individual VMwareIf you are interested in troubleshooting, and creating network maps, then I recommend that you give this Network Performance Monitor a try. Download your free trial of SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor. Once disks fill to 70% capacity they slow down dramatically. side of the coin is that a defrag can cut queues in half. am always on the lookout for such cost-nothing solutions. Starting with Windows 2000, Microsoft has licensed part ofWhat you can do is defrag a server drive-by-drive. you cannot do is schedule a defrag for the middle of the night, neither can you select multiple drives for defragging.
So the answer is to get a good third party defragger like Diskkeeper's full product. The logical solution is to buy faster disks. Go to your existing disk manufactures site and compare their figures with the data you collect PhysicalDisk: Disk Read Byte /sec Another cost-nothing solution would be to move the files or database toAlternatively you could use the load-balancing This would be my least favoured option. Technically it is a neat idea, to stripe data across two or more disks. of school days when I had to write out, 'I must not run across the schoolTo speed up the process I wrote my lines with 3 pens at once. The multiple disk controllers, like my pens, write simultaneously acrossThe reason I am wary of this method is that there is no redundancy, if any one disk fails you would lose all the data. course you could use hardware RAID 5, 10 or 20 which would protect your data against one disk failing. Diskperf's overhead is very small and my advice is to leave it turned on.

hint that this is the correct approach is that Windows 2003 has diskperf on byIf you have Windows 2000 and you do not set diskperf -y then you are storing up a problem for when you ever do need to measure disk performance. The problem is that setting diskperf needs a reboot and it would be most inconvenient when you are keen to get on with the troubleshooting. -Y Sets the system to start all disk performance counters when the system is restarted. -YD Enables the disk performance counters for physical drives. -YV Enables the disk performance counters for logical drives or storage volumes when the system is restarted. -N Sets the system to disable all disk performance counters -ND Disables the disk performance counters for physical drives. -NV Disables the disk performance counters for logical drives. \\computername Is the name of the computer you want to see or set disk performance counter use. The computer must be a Windows 2000 system.